Types of Sampling Techniques in Research Design
Types of Sampling Techniques in Research Design
Sampling entails selecting members or a subset of a target population in a study. Researchers estimate the characteristics of the entire population based on the sample and make statistical inferences regarding the whole population. Scholars and researchers must understand what research sampling is and the various methods of obtaining representative sample units to achieve their research goals and objectives. In need of data analysis services? We specialize in providing comprehensive sampling techniques to support your research needs. Our team ensures that your study receives accurate and representative data by utilizing our sampling strategies to align with your research objectives for reliable outcomes.
In research designs, sampling is a time-convenient and cost-effective technique that speeds up the research process and saves time, money, and other resources compared to studying each member of the target population.
What is Research Sampling?
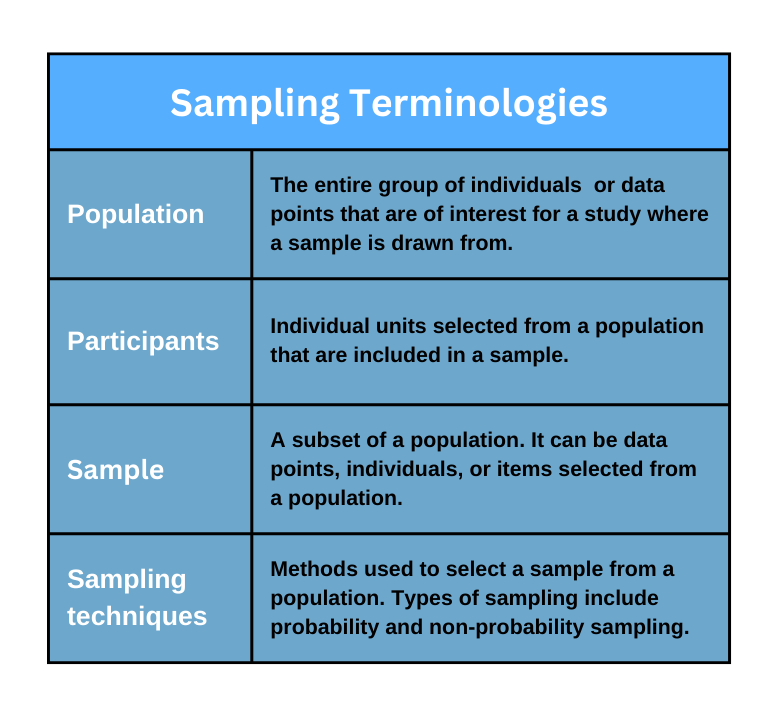
Research sampling is the process of selecting a subset or a group of participants from whom to collect data during research. The sample should be representative of the population/group from which it was drawn. There are different types of sampling methods that researchers can use to obtain representative samples. This article contains examples of the different types of sampling techniques in research design.
Methods of Sampling in Statistics
It is hardly possible to collect data from every member of the target population or group in a research study. One should select a sample or real study participants to represent the entire population/group. It is fundamental to decide on the sampling procedure that will produce an ideal representative sample to draw valid conclusions. There are two main categories of sampling in research design; probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
(1). Probability Sampling Techniques in Research
The probability sampling technique is where the researcher sets particular criteria and allows every member of the population/group an equal chance of selection to participate in the study. The probability sampling method is mostly used in quantitative research and produces rigorous statistical inferences. The main probability sampling methods include:
(a). Simple random sampling methods
The simple random sampling method is appropriate for generating results that ideally represent the entire population. The simple random sample implies that every member of the population has an equal chance of selection based on chance. The sampling procedure helps to save time and other resources during research.
For instance, if the management in a company of 300 employees offers to take employees on vacation or for team building activities, they can use the random number generator, pick pieces of paper or bottle tops out of a bowl, or any other technique entirely based on chance to give each employee an equal chance of being selected. In this example, the sampling frame should include all the members of the group (the 300 employees).
(b). Cluster sampling methods
In cluster sampling methods, the researcher devices the target population in subgroups or clusters based on demographic factors such as race, gender, or geographical location. Each subgroup should have similar features as the entire sample. If the formed clusters are too large for effective data collection, the researcher can sample individuals from each cluster or subgroup using two-stage cluster sampling methods. In the above example, if the company wishes to take 3 of the employees for vacation but it has 10 offices with almost the same number of employees with similar roles, the manager could use random sampling to select three offices (cluster sample) at a time and two-stage cluster sampling to select the 10 employees from each office (the participants) to attend the activity.
(c). Stratified random sampling
Stratified sampling is where the researcher divides the population into non-overlapping subgroups to represent the entire population. To draw precise conclusions, one should ensure that each subgroup is well represented in the random sample. The subgroups/strata can be organized depending on certain characteristics such as job roles, gender, age, or education level. If the researcher wants a gender-balanced sample from a group of 300 employees containing 200 women and 100 men, the population is divided into two strata. Stratified random sampling is then used to select 20 women and 10 men to provide a representative sample size of 30 participants.
(d). Systematic sampling techniques
In systematic sampling, the researcher enlists each target group member with a number and selects the participants at regular intervals. It is the least time-consuming random selection method owing to its predefined range. If researchers want to select a systematic sample of 30 from a population of 300 employees, they would assign numbers to each member from 1-300 and select each 10th individual to be part of the representative sample.
Probability sampling methods can be used to reduce sample bias or when dealing with a large and diverse target population. The sampling techniques help in planning and creating an accurate sample from which to derive well-defined data for the study.